This PC can't run Windows 11
It is strongly advised against installing Windows 11 on a device that falls short of meeting the minimum system requirements specified for Windows 11.
Opting to proceed with the installation on ineligible hardware entails assuming the responsibility for potential compatibility challenges that may arise. As such, users should exercise caution and be well-aware of the possible risks before attempting to install Windows 11 on a device that does not meet the prescribed criteria. Doing so could result in various issues, affecting the device's performance and functionality, thereby undermining the overall user experience.
To determine if your PC is eligible for Windows 11, you can refer to the official hardware requirements listed by Microsoft here .. If your PC does not meet any of these requirements, the installation of Windows 11 will not be possible. Checking your PC's compatibility in advance provides valuable insight into whether your computer can support the new operating system. In the event that the compatibility check returns messages such as "This PC can't run Windows 11" or "This PC doesn't currently meet all the system requirements for Windows 11," upgrading or installing Windows 11 on your PC will not be feasible. Ensuring compliance with the hardware requirements is vital for a successful and smooth transition to Windows 11, as it guarantees optimal performance and functionality on compatible devices.
If you are uncertain whether your PC satisfies the minimum system requirements for Windows 11 and you are currently using Windows 10, you can utilize the PC Health Check app to determine eligibility. This app will assess your PC and identify any components that do not meet the necessary criteria for Windows 11. By running the PC Health Check app , you can gain clarity on your device's compatibility with Windows 11 and make an informed decision regarding the upgrade. This proactive approach ensures that you have a comprehensive understanding of your PC's capability to support Windows 11, allowing you to address any potential compatibility issues before attempting the installation.
Following are the possible reasons for Windows 11 incompatibility issues:
- Secure Boot
- TPM 2.0
What is secure Boot?
Secure Boot is a robust security feature devised collaboratively by the PC industry to enhance device security by ensuring that a device initiates the boot process exclusively with software that is endorsed and trusted by the Original Equipment Manufacturer (OEM).
By validating the digital signatures of boot loaders, critical operating system files, and option ROMs, Secure Boot effectively detects any unauthorized modifications or tampering attempts. Once enabled and thoroughly configured, this feature fortifies a computer's defenses against potential attacks and malware infections. It proactively blocks detected threats from executing, thwarting any malicious activity before it can compromise the system's integrity or infect it. With Secure Boot in place, users can rely on a heightened level of protection, promoting a safer and more secure computing environment.
How to check the status of Secure Boot on your computer?
- Press Win + R to open Run window, enter "msinfo32" in the textbox and hit Enter.
- Then you will get System Information window and you can find "Secure Boot State" under System Summary.
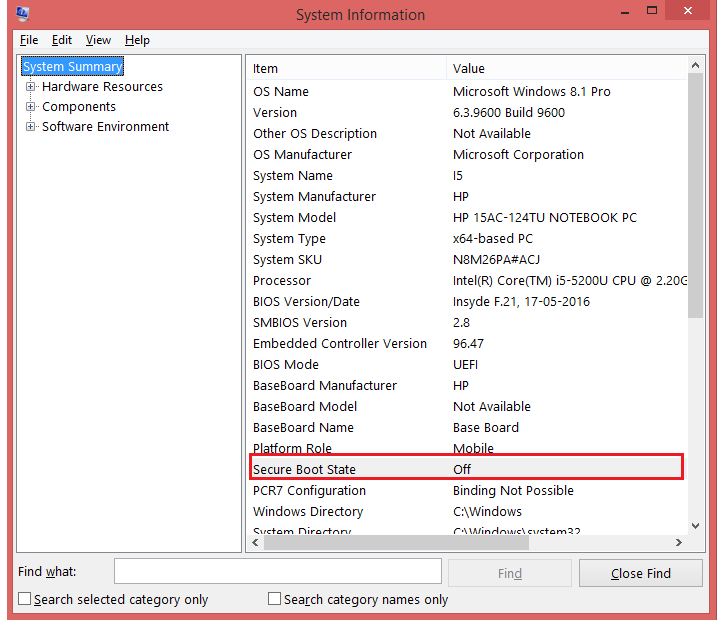
- If Secure Boot State is "On", it is enabled already; If Secure Boot State is "Off", it's disabled or not available.
What is Trusted Platform Module (TPM)?
A Trusted Platform Module (TPM) is a specialized microchip carefully designed to perform essential security-related functions, with a primary focus on encryption key management. Functioning as an endpoint device, the TPM serves as a secure repository for RSA encryption keys, specifically tailored for hardware authentication within the host system. Each TPM chip encompasses an exclusive RSA key pair known as the Endorsement Key (EK), which remains securely stored inside the chip, inaccessible to software.
Typically integrated into the motherboard of a computer or laptop, the TPM establishes communication with the rest of the system through a hardware bus. From a holistic system security perspective, TPM plays a crucial role in bolstering protection against potential threats and unauthorized access. Recognizing the major significance of TPM in reinforcing overall security, Microsoft has chosen to enforce TPM 2.0 as a requirement for Windows 11. By doing so, Microsoft aims to enhance the system's resilience against hacking attempts, augmenting the level of security and safeguarding users' data and sensitive information. By mandating TPM 2.0, Microsoft is taking proactive measures to make the task of hackers more challenging, ensuring a safer computing environment for Windows 11 users.
How to check the TPM information on your computer?
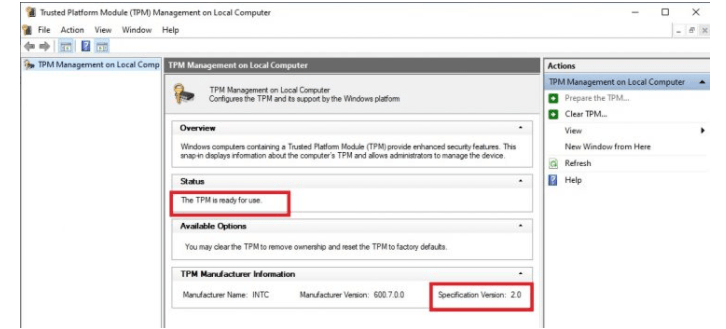
- press Win + R, type "tpm.msc" in the textox and press Enter.
- If TPM is in use and the version is 2.0, then it is compatible for Windows 11.
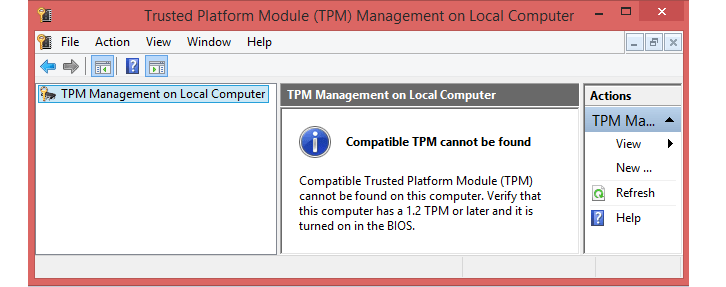
- If the TPM version is lower than 2.0, or it says "Compatible TPM cannot be found", then you are not allowed to upgraded to Windows 11.
The presence of minimum system requirements has resulted in many users encountering the "This PC can't run Windows" prompt, with the primary reason being the absence of Secure Boot or TPM 2.0. If you encounter difficulties after upgrading to Windows 11 and your device does not meet these crucial system requirements, it is advisable to revert to Windows 10. Doing so will ensure a smoother and more compatible computing experience, as Windows 10 aligns with the hardware specifications of your device. By reverting to Windows 10, you can avoid potential performance issues and incompatibilities, ensuring a stable and optimized operating system that caters to your device's capabilities.
Select Start > Settings > System > Recovery > Go back.
It is essential to note that the option to revert to Windows 10 is only accessible for a limited period of 10 days following your upgrade to Windows 11. After this designated time frame, the necessary files required to execute this function will be automatically removed from your device to optimize disk space.
Conclusion
If you wish to revert to Windows 10 and ensure a seamless transition back to the previous operating system, it is imperative to act within the specified 10-day window. By doing so, you can preserve the necessary files and effortlessly return to Windows 10, should the need arise, without encountering any potential data loss or system complications.