Difference between LAN and WAN
LAN stands for Local Area Network, and WAN stands for Wide Area Network. These two networks are categorized based on their coverage area. Local Area Networks (LANs) are designed for smaller, localized networking, commonly found in homes, businesses, schools, or within a campus. On the other hand, Wide Area Networks (WANs) cover larger areas, including cities, and enable computers in multiple geographical locations to connect and communicate.
What is LAN?
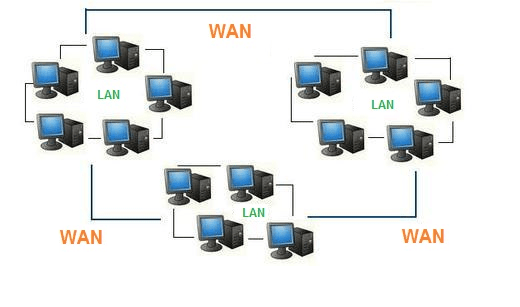
A Local Area Network (LAN) is typically built using a shared medium, where connections transmit information through devices owned and controlled by a single entity. This results in many end users sharing the same cable and being interconnected using network topologies like a bus or a ring. As a consequence, data packets sent on a LAN can be seen by all connected devices. To ensure privacy and security, each device on the LAN is equipped with a Network Interface Card (NIC) responsible for filtering out and receiving only the data packets meant for its own host, allowing for efficient communication within the network.
Every Network Interface Card (NIC) is assigned a unique hardware address known as a MAC (Media Access Control) address, which operates at the Data Link Layer of the OSI model. In Local Area Networks (LANs), ethernet communications rely on the MAC address for devices to communicate effectively. Even with various protocols like TCP/IP, DECNET, MOP, LAT, IPX, SPX, and others, these addresses are still mapped to MAC addresses. This relationship is applicable to token ring communications and other low-level protocols as well. Private addresses on a LAN are distinct from other computers in the network. At the boundary of a LAN, routers are used to connect it to the broader Wide Area Network (WAN), enabling communication between multiple geographic locations.
What is WAN?
Wide Area Network (WAN) connections span across multiple devices owned and operated by various companies and organizations. It enables access to the internet and allows users to communicate, share data, and synchronize devices with the World Wide Web (WWW). WAN connectivity is facilitated through Domain Name System (DNS) servers, which maintain records of computers and servers hosted worldwide for different services. This global network infrastructure enables seamless connectivity and access to online resources across geographical locations.
A Wide Area Network (WAN) extends over multiple geographic locations and comprises multiple interconnected Local Area Networks (LANs) using routers. Maintaining a WAN is challenging due to its vast geographical coverage. It employs layer-3 devices like routers and multi-layer switches to handle data transmission. Packets are routed in a store and forward manner, where routers receive packets and forward them to neighboring routers based on the destination address. WANs often involve third-party service providers, making them less reliable and secure compared to local networks. Ensuring the security and reliability of data transmission over such expansive networks is a complex task.

LAN - WAN Differences
| Local Area Network (LAN) | Wide Area Network (WAN) |
|---|---|
| Typically owned, controlled, and managed by a single person or organization. | Not owned by any one organization but rather exist under collective or distributed ownership and management over long distances. |
| Using Layer-2 devices like switches and bridges. Layer-1 devices like hubs and repeaters. | Using Layers-3 devices Routers, Multi-layer Switches and Technology specific devices like ATM or Frame-relay Switches etc. |
| High data transfer rate. | Lower data transfer rate compared to LANs. |
| Tend to use certain connectivity technologies, primarily Ethernet and Token Ring | Tend to use technologies like MPLS, ATM, Frame Relay and X.25 for connectivity over longer distances |
| Experiences fewer data transmission errors | Experiences more data transmission errors as compared to LAN |
| High bandwidth is available for transmission. | Low bandwidth is available for transmission. |
| Transmission medium used in LAN is co-axial or UTP cable. | WAN uses PSTN or satellite link as a transmission or communication medium. |
| Less congestion | More congestion |
- What is the main difference between the C and C++ languages?
- What is the Difference between a Curriculum Vitae and a Resume
- What is the difference between weight and mass?
- Difference Between Alternating Current (AC) and Direct Current (DC)
- What are the differences between 1G, 2G, 3G, 4G and 5G?
- What's the difference between an Intel Core i3, i5 and i7?
- What is the Difference between Internet and Intranet
- Difference between compiler and interpreter
- What Is The Difference Between Data And Information
- What is the difference between IPv4 and IPv6
- What are the differences between hardware and software
- What is the Difference Between HTTP and HTTPS?
- Difference between Windows 10 Home and Windows 10 Pro
- TCP Vs. UDP: Understanding the Difference
- What Is the Difference Between a Router and a Modem?
- Difference Between 32-Bit and 64-Bit Operating Systems