SciPy : Scientific Python
SciPy, pronounced as "Sigh Pie," is an open-source library comprising a collection of mathematical algorithms, including minimization, Fourier transformation, regression, and other essential mathematical and scientific techniques. A significant portion of SciPy's functionalities are Python "wrappers," meaning they serve as interfaces for numerical and scientific libraries that were initially implemented in Fortran, C, or C++, seamlessly integrating these powerful functionalities into Python for efficient scientific computing.
SciPy
SciPy complements the Python NumPy extension and is an integral part of the NumPy stack. It enhances NumPy's capabilities by providing optimized and additional functions commonly used in N-dimensional array manipulation and Data Science tasks. SciPy further empowers the interactive Python session by offering high-level commands and classes for data manipulation and visualization, making it a popular choice among researchers in academia and industry. Notably, SciPy has played a crucial role in significant scientific achievements, such as the detection of gravitational waves by LIGO and the imaging of a black hole in galaxy M87 by the Event Horizon Telescope. Importantly, as SciPy builds on NumPy, importing SciPy in Python eliminates the need to separately import NumPy.
SciPy - Installation
You can install SciPy in Windows via pip.
Subpackages in SciPy
| Package Name | Description |
|---|---|
| constants | Physical constants and conversion factors |
| cluster | Clustering algorithms |
| fft | Discrete Fourier Transform algorithms |
| fftpack | Fast Fourier Transforms algorithms |
| integrate | Numerical integration routines |
| interpolate | Interpolation tools |
| io | Data input and output |
| lib | Python wrappers to external libraries |
| linalg | linear algebra routines |
| misc | Miscellaneous utilities (e.g. image reading/writing) |
| ndimage | N-dimensional image processing |
| optimize | Optimization algorithms including linear programming |
| signal | Signal processing tools |
| sparse | Sparse matrix and associated algorithms |
| spatial | Spatial data structure and algorithms |
| special | Special functions |
| stats | Statistical functions |
| weave | Tool for writing C/C++ code as Python multiline strings |
These SciPy packages need to be imported before to using them.
Above code output how many cubic meters are in one liter.
SciPy Constants
You can find a large collection of mathematical and physical constants in scipy.constants. These SciPy constants can be helpful when you are working with Data Science projects.
Spatial Data
Spatial data pertains to information that is represented in a geometric space, employing various techniques like Triangulation, Voronoi Diagram, and Convex Hulls of a set of points. These spatial computations are facilitated by utilizing the Qhull library, which enables efficient handling and processing of geometric data.
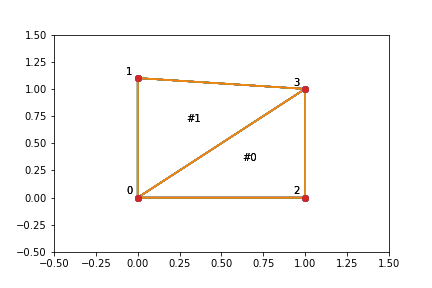
Triangulation example
In spatial data, a Triangulation of a polygon involves dividing the polygon into multiple triangles, allowing for the calculation of the polygon's area. The Delaunay() Triangulation is a method used to generate triangulations based on a set of points, creating a network of non-overlapping triangles that cover the space efficiently and are suitable for various spatial data analysis tasks.
Text
Conclusion
SciPy, short for Scientific Python, is an essential library that builds upon NumPy to provide a rich collection of mathematical algorithms and scientific tools. With its powerful functions for numerical integration, optimization, and data manipulation, SciPy serves as a crucial component of the Python ecosystem for scientific computing and data analysis.