Python Tuple
A tuple in Python is a collection of immutable objects, defined by elements separated by commas and enclosed within parentheses. The key distinction between tuples and lists is that tuples cannot be modified after creation, leading to faster tuple manipulation due to their immutability. This immutability also allows tuples to be used as dictionary keys, unlike lists. Additionally, tuples are often utilized when returning multiple results from a function, providing a convenient way to bundle and transmit multiple values.
Creating a Tuple
A tuple is defined using parentheses (). It is a collection of immutable objects separated by commas and enclosed within the parentheses. To create an empty tuple, you simply use an empty pair of parentheses.
exampleCreating Tuple with values
Python Tuple with mixed datatypes
exampleAccessing tuple values
To access specific elements within a data structure, such as a list or a tuple, we utilize square brackets [], employing a zero-based index to identify the position of the desired element. By employing the indexing mechanism, we can retrieve or manipulate individual items within the data structure, enabling precise data retrieval and modification. The zero-based indexing convention, fundamental in Python, designates the first element as index 0, the second as index 1, and so forth, offering a systematic and consistent approach to access elements within the data structure.
exampleAdding Tuple
exampleLoops and Tuple
exampleTuple print with index number
exampleConcatenation of Tuples
You can add two or more Tuples by using the concatenation operator "+".
exampleTuple length
The function len returns the length of a Tuple, which is equal to the number of its elements.
exampleSlicing Python Tuples
Python slice extracts elements, based on a start and stop.
examplestr[1:3] - The 1 means to start at second element in the Tuples (note that the slicing index starts at 0). The 3 means to end at the fourth element in the list, but not include it. The colon in the middle is how Python's Tuples recognize that we want to use slicing to get objects in the list.
exampleDelete Tuple Elements
Tuples are immutable data structures, which means that once a tuple is created, you cannot change the elements contained within it. The elements of a tuple are fixed and cannot be added, modified, or removed after the tuple is created. This immutability distinguishes tuples from lists, which are mutable and allow modifications.
If you want to remove an entire tuple, you can use the del statement followed by the tuple name. This will completely delete the tuple from memory, freeing up the resources it
exampleUpdating a Tuple
While tuples are immutable in Python, it's essential to understand that the immutability applies only to the tuple itself, not its elements. If a tuple contains mutable data types, such as lists, the nested items within those mutable data types can be changed even though the tuple remains immutable.
In other words, you cannot add, remove, or modify the elements of a tuple directly, but if an element within the tuple is a mutable data type (like a list), you can modify its contents.
exampleTuples as return multiple values
Functions are generally designed to return a single value. However, by using tuples, you can effectively bundle together multiple values into a single entity and return them together from a function.
Tuples offer a convenient way to group multiple values and return them as a single compound value. This is particularly useful when a function needs to output or return multiple pieces of related information, such as multiple results from a calculation or multiple pieces of data extracted from a dataset.
exampleNesting of Tuples
exampleConverting list to a Tuple
You can convert a List to a Tuple by using tuple()
exampleRepetition in Tuples
Using the * operator repeats a list a given number of times.
exampleTuple repetition Count
Tuple.count(x) return the number of times x appears in the Tuple.
examplezip() function
The zip() function is used to combine two or more sequences, such as lists or tuples, into a single iterable of tuples. Each tuple contains elements from corresponding positions of the input sequences. This is particularly useful when you want to loop over multiple sequences simultaneously and process their elements together.
exampleTuple min(), max()
The min() returns the minimum value from a tuple and max() returns the maximum value from the tuple.
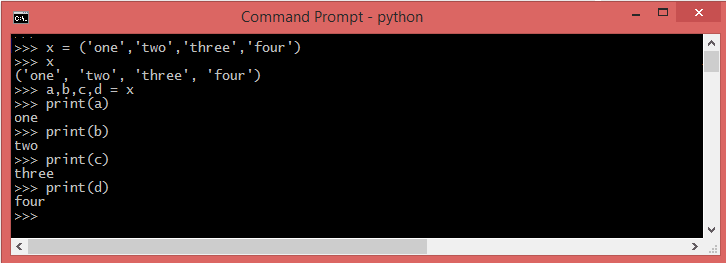
exampleTuple Packing and Unpacking
Packing of tuples refers to the process of creating a tuple by comma-separating multiple items within parentheses (). The items enclosed within the parentheses are automatically packed together to form a single tuple. For example:
Conclusion
A tuple is an immutable collection of objects, defined by elements separated by commas and enclosed within parentheses (). Once a tuple is created, its elements cannot be modified, making tuples suitable for representing fixed data or information that should remain constant throughout the program's execution. Tuples are useful for efficient data storage, as dictionary keys, and when returning multiple results from a function, due to their immutability and ability to hold multiple values in a structured manner.