What is .Net serialization
.NET serialization is the process of converting an object's state into a binary format that can be stored, transmitted, or persisted, and then restoring the object's state back from the binary format. It is a fundamental technique used in .NET for data storage, inter-process communication, distributed computing, and object persistence.
Serialization
Serialization plays a crucial role when objects need to be transmitted over a network, shared between different processes or applications, or saved to a file or a database. By converting objects into a serialized form, they can be easily transmitted or stored, and later deserialized to recreate the original object.
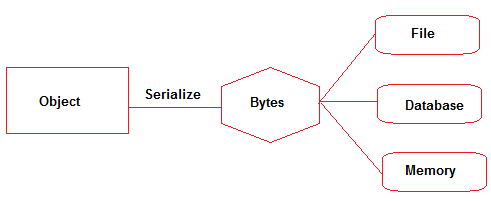
In .NET, serialization is primarily achieved through two mechanisms: Binary Serialization and XML Serialization. Let's explore each of them in detail:
Binary Serialization
Binary serialization in .NET involves converting objects into a binary format using the BinaryFormatter class. This format is compact and optimized for performance. The BinaryFormatter serializes an object graph by traversing its members and writing their values to a binary stream.
XML Serialization
XML serialization in .NET involves converting objects into an XML-based format using the XmlSerializer class. The XmlSerializer serializes an object graph by representing its properties, fields, and values as XML elements and attributes.
Both binary serialization and XML serialization have their advantages and are suitable for different scenarios. Binary serialization offers better performance and smaller output size, but the resulting format is not human-readable. XML serialization, on the other hand, produces human-readable XML files that can be easily understood and manipulated but at the cost of larger file size and reduced performance.
Conclusion
Serialization is a powerful feature in .NET that enables objects to be easily persisted, transmitted, and reconstructed. It plays a vital role in scenarios such as distributed systems, web services, caching, and data storage, allowing objects to retain their state across different boundaries and facilitating seamless communication between different components and systems.
- C# Interview Questions (part-1)
- C# Interview Questions (part-2)
- C# Interview Questions (part-3)
- Difference between a Debug and Release build
- Difference between normal DLL and .Net DLL
- What is an Interface in C#
- Difference between Abstract Class and Interface in C#
- Difference between a thread and a process
- Delegates in C# with Examples
- Differences between a control and a component
- Differences between Stack and Heap
- What is .Net Reflection
- Globalization and Localization | C#
- Difference between web service and .net remoting
- Difference between managed and unmanaged code
- Difference between Shallow copy and Deep copy
- Use of System.Environment Class
- What is the difference between private and shared assembly?
- Does the .NET have in-built support for serialization?
- How to properly stop the Thread in C#?
- Why are there five tracing levels in System.Diagnostics.TraceSwitcher?
- Why is XmlSerializer so slow?
- How many types of Jit Compilers?