Difference between web service and .net remoting
What is Web services ?
A web service is a communication method between software units that operates over the World Wide Web. It allows applications to interact with each other using various data formats such as HTTP, XML, and SOAP, without concerning themselves with the underlying implementation details of each specific web service.
XML is utilized to structure and annotate the data exchanged between web services. SOAP serves as the protocol for transmitting this data, ensuring reliable and secure communication. WSDL plays a significant role by providing a standardized description of the available web services, allowing clients to understand their functionalities and access them programmatically. UDDI complements this by providing a directory or registry of available web services, facilitating their discovery and integration into applications.
Unlike traditional graphical user interfaces, web services focus on sharing business logic, data, and processes through a programmatic interface across a network. This allows applications to use the functionality and capabilities offered by web services to enhance their own operations and provide seamless integration with other systems and services.
What is .Net Remoting ?
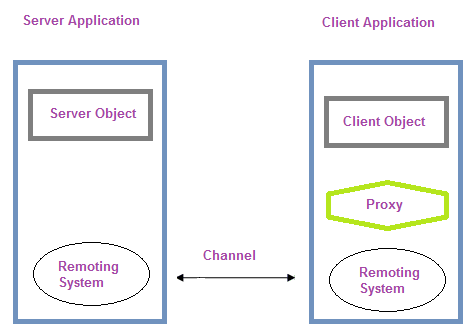
.NET Remoting is a powerful communication framework that enables seamless interaction between objects across different application domains, regardless of whether the application components are co-located on a single computer or distributed across various geographical locations. It provides a high-level abstraction that shields developers from the complexities associated with managing connections, handling data marshaling, and dealing with XML and SOAP protocols.
With .NET Remoting, developers can focus on designing and implementing the functionality of their distributed applications, without having to worry about the intricacies of low-level networking and communication protocols. The framework abstracts away the complexities by providing a transparent and efficient means of communication between remote objects, allowing them to exchange data and invoke methods as if they were locally accessible.
You can study more in detail about .Net Remoting with sample Source code :
C# Remoting Architecture VB.Net Remoting ArchitectureWhich one is better ?
Both web services and .NET Remoting are robust technologies that offer effective frameworks for developing distributed applications. Web services are particularly suitable for scenarios where the XML Schema type system is preferred, providing a simple programming model with extensive cross-platform compatibility. On the other hand, .NET Remoting is designed to utilize the runtime type system and offers a more intricate programming model, albeit with more limited reach.
When considering the deployment scenario, if both the clients and components reside within the same firewall, web services can be a suitable choice. However, it's important to note that in this case, all data communication would flow through a web server, which may introduce performance overhead. On the other hand, .NET Remoting facilitates communication between client applications and components using a binary format. This approach is more advantageous for achieving high-speed, efficient communication between proprietary .NET components, typically over an internal network.
It is important to understand how both technologies work and to choose the one that is right for your application.
Conclusion
Web services excel in scenarios that prioritize compatibility and interoperability across different platforms, while .NET Remoting is more suitable for achieving optimized binary communication between closely coupled .NET components within a controlled network environment. Careful consideration of the specific requirements and constraints of the project will help determine which technology is the most appropriate for a given distributed application.
- C# Interview Questions (part-1)
- C# Interview Questions (part-2)
- C# Interview Questions (part-3)
- Difference between a Debug and Release build
- Difference between normal DLL and .Net DLL
- What is an Interface in C#
- Difference between Abstract Class and Interface in C#
- Difference between a thread and a process
- Delegates in C# with Examples
- Differences between a control and a component
- Differences between Stack and Heap
- What is .Net Reflection
- Globalization and Localization | C#
- What is .Net serialization
- Difference between managed and unmanaged code
- Difference between Shallow copy and Deep copy
- Use of System.Environment Class
- What is the difference between private and shared assembly?
- Does the .NET have in-built support for serialization?
- How to properly stop the Thread in C#?
- Why are there five tracing levels in System.Diagnostics.TraceSwitcher?
- Why is XmlSerializer so slow?
- How many types of Jit Compilers?