LinkedList in Java
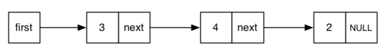
linked lists are a fundamental and widely used data structure that differs from arrays in the way they allocate and store data. While arrays allocate memory for all elements together in a contiguous block, linked lists allocate separate memory blocks, called nodes, for each element.This allows linked lists to be dynamically extended or reduced to accommodate varying data sets, unlike static arrays.
However, linked lists lack direct access to individual elements, requiring traversal from the head node to reach a specific item. Despite this limitation, linked lists provide flexibility and efficient insertion and removal operations, making them valuable in scenarios where dynamic data manipulation is required.
Creating a LinkedList
In this example, we create a LinkedList that stores elements of type String.
Adding Elements to the LinkedList
We can add elements to the LinkedList using the add() method. In this case, we add three fruits to the list.
Accessing Elements in the LinkedList
We can access elements in the LinkedList using the get() method, which takes the index of the element as an argument. In this example, we retrieve the first element in the list.
Modifying Elements in the LinkedList
We can modify elements in the LinkedList using the set() method, which takes the index of the element to be modified and the new value as arguments. In this case, we change the second element to "grape".
Removing Elements from the LinkedList
We can remove elements from the LinkedList using the remove() method, which takes the index of the element to be removed as an argument. In this example, we remove the third element from the list.
Iterating over the LinkedList
We can iterate over the elements of the LinkedList using a for-each loop. This allows us to access and process each element in the list.
LinkedList | Java Source Code
The following Java program illustrates several of the methods supported by this LinkedList collection Framework.
Conclusion
The LinkedList class in Java is an implementation of the List interface that provides a doubly-linked list data structure. It allows efficient insertion and removal of elements at both the beginning and end of the list, making it suitable for scenarios where frequent modifications are required.