Object-Oriented Programming
The principles of Object-Oriented Programming form the foundational framework for numerous contemporary programming languages. At the heart of Object-Oriented Programming lies the fundamental concept of an Object. An Object represents a cohesive unit comprising both data and the corresponding methods (functions) that manipulate this data. The essence of an Object-Oriented Programming language revolves around the amalgamation of data and methods into a singular entity.
Encapsulating data
By encapsulating data and methods within an Object, the access to data is restricted solely through its associated methods, safeguarding its integrity from inadvertent modifications. This encapsulation process, which combines data and methods into a unified unit, is referred to as Data Encapsulation, and the practice of concealing data is known as Data Hiding. These concepts encapsulate the essence of an Object-Oriented Language, emphasizing the cohesive and secure handling of data through encapsulation and abstraction.
An object serves as a representation of a real-world entity, embodying two fundamental aspects: state and behavior. Just like real-world objects, software objects possess state and behavior. State refers to the data associated with an object, which is stored in fields or variables. Behavior, on the other hand, encompasses the actions or operations that an object can perform, which are exposed through methods or functions. Methods operate on the internal state of an object and facilitate communication between objects. By encapsulating both state and behavior, objects provide a powerful mechanism for modeling and interacting with entities in software systems, mirroring the characteristics and functionality found in the physical world.
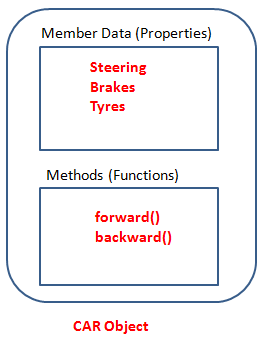
In the given example, we observe the association between a real-world entity (CAR) and Object-Oriented Programming. The CAR represents an object that encompasses various properties, such as Steering, Brakes, and Tires, along with corresponding functions or methods like forward() and backward(). This demonstrates the concept of encapsulating properties and functions within a single unit, enabling the functions to operate in conjunction with the properties.

Conclusion
It is important to note that the .NET Framework is built upon the fundamental principles of Object-Oriented Programming. It extensively supports all the essential features of an object-oriented programming language, including encapsulation, inheritance, and polymorphism. These features play a key role in structuring software systems within the .NET Framework, facilitating code organization, reusability, and modularity. By using these object-oriented concepts, developers can design robust and maintainable applications that adhere to industry best practices.
- What are the different types of inheritance ?
- What are Access Modifiers ?
- Why Classes cannot be declared as Protected?
- Can we declare private class in namespace
- Difference between Classes and Structures
- Can we use pointers in C# ?
- Why abstract class can't create instance
- Can you prevent your class from being inherited
- Difference between method Overloading and Overriding
- Difference between Early Binding and Late binding
- What is nested class
- What is partial class ?
- What is Virtual Method
- Difference between class and object
- What is Data Encapsulation?
- Object Based Language and OOPs
- SOLID Principles in C#
- Solid Principles | Advantages and Disadvantages