Page Directives in Asp.Net
Directives in ASP.NET are statements that provide optional settings and instructions for the ASP.NET framework, without being included in the rendered HTML output sent to the client's browser. These directives encompass various functionalities such as registering custom controls and specifying the page language. They play a crucial role in defining the processing behavior of .aspx pages (web forms) or .ascx pages (user controls) within the .NET framework.
directive
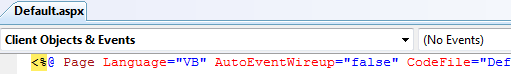
The most commonly used directive is the @ Page directive and it can be used only in Web Forms. Page directive allows you to specify many configuration options for the page. By default, Visual Studio creates a page directive as shown below:
In an .aspx file, it is recommended to have only one @ Page directive. Within this directive, it is important to specify the desired language using the Language attribute. This attribute supports various .NET Framework-supported languages such as VB.Net, C#, or JScript.
The AutoEventWireup attribute controls the automatic binding of page events based on the method naming convention. By default, it is set to true, enabling automatic lookup and binding of events. However, if set to False, explicit binding of methods to page events is required, allowing flexibility in naming conventions.
The CodeFile attribute is used to specify the path to the referenced code-behind file associated with the page. On the other hand, the Inherits attribute identifies the class name from which the page should inherit. This allows for customization by deriving from any class based on the Page class.
Different types of directives in Asp.Net
@ Assembly
The @Assembly Directive attaches assemblies to the page or an ASP.NET user control thereby all the assembly classes and interfaces are available to the class. This directive supports the two attributes Name and src. The Name attribute defines the assembly name and the src attribute defines the source of the assembly.
@ Control
Defines control-specific attributes used by the ASP.NET page parser and compiler and can be included only in .ascx files (user controls).
@ Implements
The @Implements Directive gets the ASP.NET pages to implement .Net framework interfaces. This directive only supports a single attribute interface.
@ Import
The Import directive imports a namespace into a web page, user control page of application. If the Import directive is specified in the global.asax file, then it is applied to the entire application. If it is in a page of user control page, then it is applied to that page or control.
@ Master
Identifies a page as a master page and defines attributes used by the ASP.NET page parser and compiler and can be included only in .master files.
@ MasterType
Defines the class or virtual path used to type the Master property of a page.
@ OutputCache
The OutputCache directive controls the output caching policies of a web page or a user control.
@ Page
The @Page directive enables you to specify attributes and values for an Asp.Net Page to be used when the page is parsed and compiled. Every .aspx files should include this @Page directive to execute. There are many attributes belong to this directive.
@ PreviousPageType
Creates a strongly typed reference to the source page from the target of a cross-page posting.
@ Reference
Links a page, user control, or COM control to the current page or user control declaratively.
@ Register
Associates aliases with namespaces and classes, which allow user controls and custom server controls to be rendered when included in a requested page or user control.
- Asp.Net Interview Questions (Part-1)
- Asp.Net Interview Questions (Part-2)
- Advantages of ASP.NET Web Development
- What is IIS - Internet Information Server
- What is Virtual Directory
- What is HttpHandler
- What is a postback
- What is IsPostBack
- What is global.asax
- Difference between Machine.config and web.config
- Difference between HTML control and Web Server control
- What is Query String
- Difference between Authentication and Authorization
- How to secure Connection Strings
- What is ASP.Net tracing
- Passing values between Asp.Net pages
- Differentiate between client side validation and server side validation
- How to Get host domain from URL
- Adding a Favicon To Your Website
- Asp.Net Textbox value in Javascript
- AutoEventWireup attribute in ASP.NET
- Can I use multiple programming languages in a ASP.net Web Application?
- Difference: Response.Write and Response.Output.Write
- How many web.config files can I have in an application?
- What is Protected Configuration in asp.net?
- Static variablesin .Net , what is their life span?
- Difference between ASP Session and ASP.NET Session?
- What does mean Stateless in Asp.Net?
- What is the Difference between session and caching?
- What are different types of caching using cache object of ASP.NET?
- Which method is used to remove the cache object?
- How many types of Cookies are available in ASP.NET?
- What is Page Life Cycle in ASP.net?
- What is the code behind and Inline Code in Asp.Net?
- What is master page in ASP.NET?
- Can you change a Master Page dynamically at runtime?
- What is cross-page posting in ASP.NET?
- How to redirect a page in asp.net without performing a round trip ?
- How to register custom server control on ASP.NET page?
- How do you validate Input data in Asp.Net?
- What's the difference between ViewData and ViewBag?
- Difference between Response.Redirect and Server.Transfer
- What is the function of the CustomValidator control?
- Define RequiredFieldValidator?
- Difference between custom control and user control
- Difference between Label and Literal control in ASP.Net
- What are the major events in Global.Asax file?
- What is Event Bubbling in asp.net ?
- What is Delay signing?
- What is the difference between in-proc and out-of-proc?
- What is the difference between POST and GET?
- A potentially dangerous Request.Form value was detected from the client