Python range() function
The Python built-in function, range(), serves the purpose of generating a sequence of numerical values. It constructs a collection of integers, commencing from a predefined lower bound (typically 0) and extending up to a designated upper boundary, potentially advancing in specified increments (defaulting to 1). Although the mechanics differ slightly between Python 2.x and Python 3.x, the fundamental concept remains consistent.
Syntax- start - The starting point for the range() to generate numbers.
- stop - It is the point just before range() ends. The range of integers end at stop - 1.
- step (Optional) - integer value which determines the increment between each integer in the sequence.
Using only stop parameter
In this example, the range() function generates numbers from 0 up to (but not including) 5.
Using start and stop parameters
Here, the sequence starts from 2 and goes up to (but not including) 8.
Using start, stop, and step parameters
In this example, the sequence starts from 1, goes up to (but not including) 10, with a step of 2.
Creating a list from a range()
You can convert a range() object to a list using the list() constructor.
Incrementing with positive step
Decrementing with negative step
How to floats with Python's range() function
Unfortunately Python range() function doesn't support the float numbers. i.e. user cannot use floating point number in any of its argument.
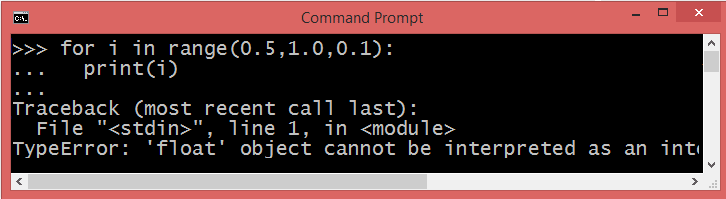
If you provide a non-integer stop value, then it raises a TypeError: 'float' object cannot be interpreted as an integer .
However, you can implement an alternate way to get the range of floating numbers .
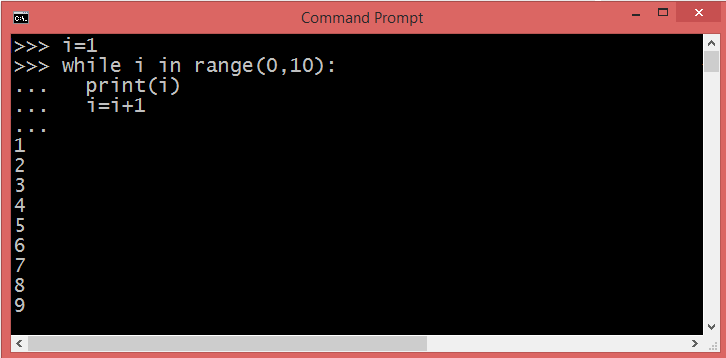
Python while loop using range() function
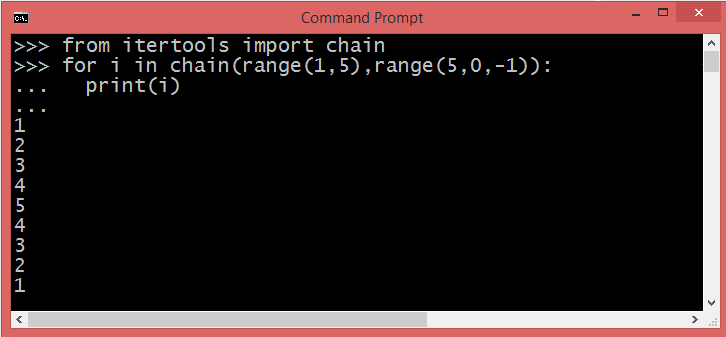
Concatenation of two range() functions using chain() method
The chain() method takes any number of iterables as arguments and "chains" them together.
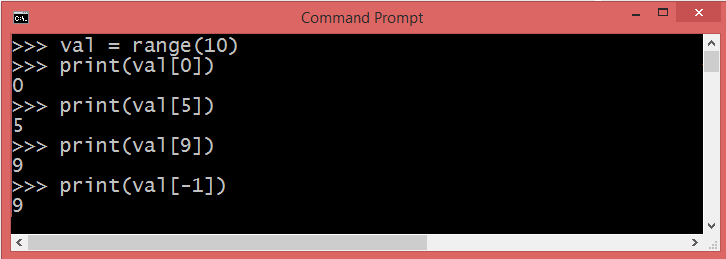
Accessing Python range() values using index
Python range() to List
The Python range type represents an immutable sequence of numbers, so it is possible to convert the output of a range() to the Python list.
Conclusion
The Python range() function facilitates the creation of sequences of numbers, offering control over the start, end, and step size of the sequence. It efficiently generates values on demand, serving as a memory-efficient tool for looping and iteration tasks.
- How to use Date and Time in Python
- Python Exception Handling
- How to Generate a Random Number in Python
- How to pause execution of program in Python
- How do I parse XML in Python?
- How to read and write a CSV files with Python
- Threads and Threading in Python
- Python Multithreaded Programming
- How to Convert a Python String to int
- Python filter() Function
- Difference between range() and xrange() in Python
- How to print without newline in Python?
- How to remove spaces from a string in Python
- How to get the current time in Python
- Slicing in Python
- Create a nested directory without exception | Python
- How to measure time taken between lines of code in python?
- How to concatenate two lists in Python
- How to Find the Mode in a List Using Python
- Difference Between Static and Class Methods in Python?