HTTP Error 403.14 - Forbidden
The HTTP error 403 - Forbidden typically indicates that the server has understood the request, but it refuses to fulfill it due to restricted access to the requested file or folder. This denial of access can occur intentionally, where the site owner has limited permissions, or it may be a result of misconfiguration. The server acknowledges the request, but it explicitly denies access to the resource, preventing the user from viewing or interacting with it.
For end-users
The vast majority of the time, there's not much you can do to fix things on your end. Still, there are some things you can try.
- Refresh the Page
- Double Check the Address
- Clear Browser Cookies and Cache
- Check firewall settings
- Deactivate browser extensions
- Try Again Later
- Contact website administrators
For site administrators
There are three common causes for this error
- An empty website directory
- No index page
- Permission and Ownership error
An empty website directory
Make sure that your website content has been uploaded to the correct directory on your server.
Plesk server
When creating a website using Plesk, the platform not only sets up a new virtual host on the web server but also generates the necessary directory structure for the site. Additionally, Plesk populates these directories with specific initial content, ensuring that the website has the required files and data to function properly. This streamlined process simplifies website creation and setup for users, providing them with a functional site from the start.These directories are located in the corresponding virtual host directories :
On Linux: /var/www/vhosts/
On Windows: C:\inetpub\vhosts\
By default it creates the directories below:
- domain's root directory (may be changed in the Domains > example.com > Hosting Settings);/var/www/vhosts/example.com/httpdocs/
When you connect with your FTP user, you just need to navigate into the httpdocs directory. Moreover, be sure to replace example.com with your actual domain name.
cPanel server:
In Plesk, the /home/example/public_html/ folder serves as the web root for your primary domain name. This means that any files placed in the public_html folder will be accessible and displayed when someone enters your main domain name into their web browser. Essentially, the content within the public_html directory is what visitors will see when they access your website.
When you connect with your FTP user, you just need to navigate into the public_html directory. Be sure to replace example with the name of your cPanel account username.
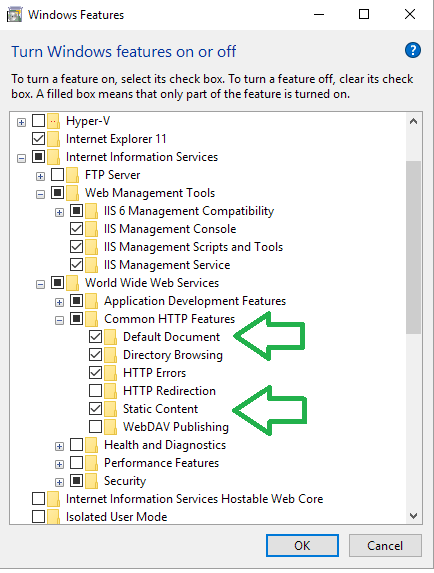
IIS:
Microsoft turn off the most basic features by default. Go to Turn Windows features on or off.

No index page
The default document on a web server is the initial file that is sent to visitors when they access your website. Typically, the default document is set to index.html or index.php, but it can be customized to any desired file. This ensures that when someone visits your site, the specified default document is displayed as the starting point of the website.
Index files option is set to Default at:
Linux: Domains > example.com > Apache & Nginx Settings
Windows: Domains > example.com > IIS Settings
To resolve this 403 Forbidden error, upload an index page to your httpdocs or public_html directory.
If you already have a home page called something else - example.html , you have a couple of options to change it:
- Rename your home page to index.html or index.php.
- Set up a redirect on the index page to your real home page.
- Set a different default home page in your .htaccess file.
HTTP Error 403.14 - Forbidden in IIS
The Web server is configured to not list the contents of this directory.In IIS, a default document is not configured for the requested URL, and directory browsing is not enabled on the server.
How to enable directory browsing?- Go to the IIS Express install directory.
- Run appcmd set config /section:system.webServer/directoryBrowse /enabled:true to enable directory browsing at the server level.
- Run appcmd set config ["SITE_NAME"] /section:system.webServer/directoryBrowse /enabled:true to enable directory browsing at the site level.
Moreover, verify that the configuration/system.webServer/directoryBrowse@enabled attribute is set to true in the site or application configuration file
Permissions and ownership errors
HTTP Error 403.14 – Forbidden error can also be caused by incorrect ownership or permissions on your website content files and folders.
Permissions
- for directories
find /desired_location -type d -print0 xargs -0 chmod 0755
- for files
find /desired_location -type f -print0 xargs -0 chmod 0644
Additionally, if you know PHP runs as the user and not as "apache", then you can set PHP files to 600, for an extra level of security, eg:
find . -type f -name '*.php' -exec chmod 600 {} \;
Ownership
The concept of owner and groups for files is fundamental to Linux. Every file is associated with an owner and a group. You can use chown and chgrp commands to change the owner or the group of a particular file or directory.
Every Linux system have three types of owner:
- User: A user is the one who created the file. By default, whosoever, creates the file becomes the owner of the file. A user can create, delete, or modify the file.
- Group: A group can contain multiple users. All the users belonging to a group have same access permission for a file.
- Other: Any one who has access to the file other than user and group comes in the category of other. Other has neither created the file nor is a group member.
Users and groups can be locally managed in /etc/psswd or /etc/group .
Plesk server: domain - example.com, domainuser - FTP usercPanel server: account user - example/var/www/vhosts/example.com/ - root:root
/var/www/vhosts/example.com/httpdocs/ - domainuser:psaserv
/var/www/vhosts/example.com/httpdocs/index.html - domainuser:psacln
/home - root:root
/home/example - example:example
/home/example/public_html - example:example
The chown command is used to change file ownership settings. The basic syntax is:
chown owner-user file
chown owner-user:owner-group file
chown owner-user:owner-group directory
chown options owner-user:owner-group file
Nginx 403 forbidden error
![Nginx 403 forbidden for all files, Nginx 403 error: directory index of [folder] is forbidden](img/nginx-403.png)
The Nginx 403 Forbidden error is a status code that occurs when a client attempts to access a part of the web server without sufficient permissions. When Nginx accesses a directory, it typically tries to index it and provide a list of files inside to the browser/client. However, directory indexing is usually disabled by default, leading to the error message "Nginx 403 error: directory index of [folder] is forbidden." This error indicates that the client does not have the required permissions to access the directory or view its contents.
Incorrect Index File
The try_files directive in Nginx attempts to serve files in the order they are specified and sets the internal file pointer accordingly. If you are experiencing issues with directory indexing being turned off and encountering the Nginx 403 Forbidden error, it is likely due to the presence of a directory option in the try_files directive. This can prevent proper file serving and lead to the forbidden error when accessing directories without sufficient permissions.
to
Incorrectly set permissions
To resolve the Nginx 403 Forbidden error that may arise from incorrectly set permissions, you can follow these steps:
- Change the directory permissions to 755 and the file permissions to 644. This can be done using the "chmod" command in the terminal or command prompt.
- Ensure that the user running the Nginx process has ownership of the files and directories. For example, you can set the user to "www-data" using the "chown" command.
By setting the correct permissions and ownership, you should be able to resolve the 403 Forbidden error and allow Nginx to serve the files and directories properly.
Finally, set the directory and file permissions as:
Conclusion
HTTP error 403 - Forbidden indicates that the server understood the request, but it refuses to fulfill it due to insufficient permissions. The client attempting to access a specific part of the webserver is denied access, either intentionally or due to misconfigured permissions.
- How to Print Screen
- How to View Hidden Files in Windows 11, 10, 8 and 7
- Fahrenheit to Celsius Temperatire Conversion Formula
- How to zip files - Compress and uncompress files
- How to Use Robocopy
- How to WMIC ?
- How to recover deleted files
- Microsoft Outlook POP3 Settings, Microsoft Outlook IMAP Settings
- How to Update Windows 11
- What is Three-Tier Architecture ?
- What Is an API (Application Program Interface) ?
- Differences Between HTML4 And HTML5
- How to choose the best antivirus software
- How to Embed a YouTube Video in Your Website
- what is the difference between x64 and x86
- Learn Multiplication of Tables
- What is a Proxy Server?
- How to use a Google Android phone as a Wi-Fi hotspot
- How to automatically redirect a Web Page to another URL
- How to Download YouTube Videos
- What is a Phishing Attack ? How can I avoid them?
- What is a Call To Action?
- What's the Difference Between JPG and PNG?
- What Is a "500 Internal Server Error" and How Do I Fix It?
- What is the difference between OTF and TTF fonts
- How to enable flash player on chrome
- How to Select a Video Editing Software
- Why am I getting a "Your connection is not private error" in Chrome
- How to block "Deceptive site ahead" security error?
- Crypto for beginners: What is cryptocurrency?
- What is Bitcoin and how does it work?
- How to fix HTTP Error 502 Bad gateway
- GET url returns "data:text/html,chromewebdata"
- Chrome:Your Clock Is Ahead / Your Clock Is Behind Error
- How to fix ERR_UNKNOWN_URL_SCHEME
- SSL Error on Port 443
- How to Fix This Site Can't Be Reached Error in Chrome
- A disk read error occurred, Press Ctrl+Alt+Del to restart
- How to use System Restore on Windows 10
- What is HTTP error 503 and how do you fix it?
- How to get help in Windows 10
- How To Disable Windows 10 Forced Updates
- How to Fix Google Chrome Error - ERR_SSL_PROTOCOL_ERROR
- How to reset windows 10 password
- What is Blockchain?
- How To Fix: ERR_PROXY_CONNECTION_FAILED
- Unable to send mail through smtp.gmail.com
- How to fix DNS_PROBE_FINISHED_NXDOMAIN
- How to use GTMetrix to Speed up Your Website?
- How to fix System Thread Exception Not Handled Error
- How to fix ERR_INTERNET_DISCONNECTED Error
- WiFi Connected But No Internet Access – How to Fix?
- How to fix a HTTP Error 400: Bad Request?
- What is Deprecation
- What is the maximum length of a URL in different browsers?
- SSL Certificate Problem: Unable to get Local Issuer Certificate
- How to Fix the ERR_CONNECTION_TIMED_OUT Error
- What does localhost:8080 mean?
- How to reduce initial server response time
- 414 Request-URI Too Long - HTTP
- Message channel closed before a response was received