What is __init__.py for?
The __init__.py file is used to indicate that a directory should be considered a Python package. It is a special file that Python looks for when importing modules from a package. The presence of an __init__.py file in a directory signifies that the directory should be treated as a package, and it can contain initialization code, package-level attributes, and submodules.
The following image shows the structure of a standard Python module.
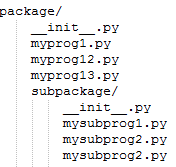
Following are some key points about the __init__.py file in Python:
Package Initialization
When Python encounters an __init__.py file in a directory, it recognizes that directory as a package. This allows you to organize related modules and subpackages in a structured manner.
Namespace Package
In Python 3.3 and later, an empty __init__.py file can also indicate a "namespace package." Namespace packages are used to spread a package across several directories or even in different locations, enabling modular distribution and installation of libraries.
Initialization Code
You can include initialization code, variables, and functions in the __init__.py file. This code is executed when the package is imported. It's a convenient place to perform setup tasks for the package.
Access to Submodules
The __init__.py file can also import and define attributes or submodules that are available when the package is imported. This can provide a more organized and clean interface for users of the package.
Example of a package directory structure:When you import the package using import my_package, the code in my_package/__init__.py will be executed, and the submodules module1 and module2 will be accessible as my_package.module1 and my_package.module2.
Conclusion
The __init__.py file is used to mark a directory as a Python package, define initialization code, and provide a way to organize and structure modules and submodules within the package.
- Python Interview Questions (Part 2)
- Python Interview Questions (Part 3)
- What is python used for?
- Is Python interpreted, or compiled, or both?
- Explain how python is interpreted
- How do I install pip on Windows?
- How do you protect Python source code?
- What are the disadvantages of the Python?
- How would you achieve web scraping in Python?
- How to Python Script executable on Unix
- What is the difference between .py and .pyc files?
- What does __name__=='__main__' in Python mean?
- What is docstring in Python?
- What is the difference between runtime and compile time?
- How to use *args and **kwargs in Python
- Purpose of "/" and "//" operator in python?
- What is the purpose pass statement in python?
- Why isn't there a switch or case statement in Python?
- How does the ternary operator work in Python?
- What is the purpose of "self" in Python
- How do you debug a program in Python?
- What are literals in python?
- Is Python call-by-value or call-by-reference?
- What is the process of compilation and Loading in python?
- Global and Local Variables in Python
- Static analysis tools in Python
- What does the 'yield' keyword do in Python?
- Python Not Equal Operator (!=)
- What is the difference between 'is' and '==' in python
- What is the difference between = and == in Python?
- How are the functions help() and dir() different?
- What is the python keyword "with" used for?
- Why isn't all memory freed when CPython exits
- Difference between Mutable and Immutable in Python
- Python Split Regex: How to use re.split() function?
- Accessor and Mutator methods in Python
- How to Implement an 'enum' in Python
- What is Object in Python?
- How to determine the type of instance and inheritance in Python
- Python Inheritance
- How is Inheritance and Overriding methods are related?
- How can you create a copy of an object in Python?
- Class Attributes vs Instance Attributes in Python
- Static class variables in Python
- Difference between @staticmethod and @classmethod in Python
- How to Get a List of Class Attributes in Python
- Does Python supports interfaces like in Java or C#?
- How To Work with Unicode strings in Python
- Difference between lists and tuples in Python?
- What are differences between List and Dictionary in Python
- Different file processing modes supported by Python
- Python append to a file
- Difference Between Multithreading vs Multiprocessing in Python
- Is there any way to kill a Thread in Python?
- What is the use of lambda in Python?
- What is map, filter and reduce in python?
- Is monkey patching considered good programming practice?
- What is "typeerror: 'module' object is not callable"
- Python: TypeError: unhashable type: 'list'
- How to convert bytes to string in Python?
- What are metaclasses in Python?