Character Stream Vs Byte Stream in Java
A stream in Java is a mechanism for sequentially accessing data from various sources, such as files, arrays, devices, and programs. While streams allow data processing on a per-item basis, they do not support bulk operations. It is essential to distinguish between byte streams and character streams since Java treats bytes and characters differently. Consequently, Java defines two types of streams: Byte Streams, primarily for binary data, and Character Streams, designed specifically for textual data processing, ensuring efficient and accurate handling of diverse data types in the language.
Byte Streams
A byte stream facilitates file access on a byte-by-byte basis and is commonly used for input and output operations involving 8-bit bytes. While byte streams are versatile and suitable for various file types, they may not be ideal for handling text files efficiently, especially if they use Unicode encoding, where characters are represented by two bytes. In such cases, manual conversion becomes necessary. It is important to note that byte-oriented streams do not employ any specific encoding scheme, whereas character-oriented streams adopt UNICODE encoding for seamless handling of textual data. Additionally, all byte stream classes in Java are derived from the InputStream and OutputStream classes, forming the foundation of byte stream handling in the language.
ExampleWhen to use:
Byte streams should only be used for the most primitive I/O
When not to use:
You should not use Byte stream to read Character streams
e.g. To read a text file
Character Streams
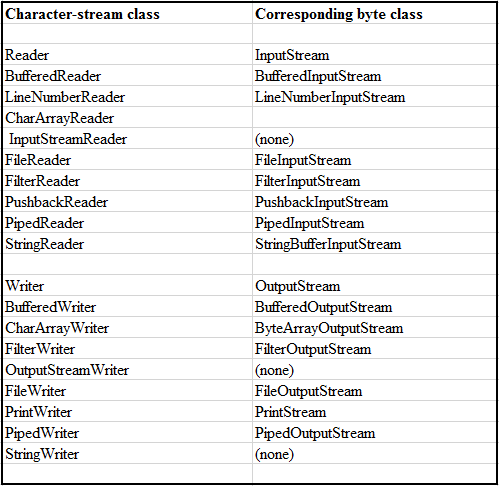
A character stream operates by reading a file character by character. Character streams are considered higher-level compared to byte streams, as they encompass byte streams wrapped with additional logic to enable output of characters based on a specific encoding. Thus, for proper functionality, a character stream requires knowledge of the file's encoding. Character streams are versatile and capable of handling various character sets, including ASCII, Unicode, UTF-8, UTF-16, and more. All character stream classes in Java are derived from the Reader and Writer classes, forming the foundation of character stream handling in the language.
ExampleWhen to use:
To read character streams either from Socket or File of characters
Conclusion
- Character oriented are tied to datatype. Only string type or character type can be read through it while byte oriented are not tied to any datatype, data of any datatype can be read(except string) just you have to specify it.
- Character oriented reads character by character while byte oriented reads byte by byte.
- Character oriented streams use character encoding scheme(UNICODE) while byte oriented do not use any encoding scheme.
- Character oriented streams are also known as reader and writer streams Byte oriented streams are known as data streams-Data input stream and Data output stream.
- Java Interview Questions-Core Faq - 1
- Java Interview Questions-Core Faq - 2
- Java Interview Questions-Core Faq - 3
- Features of Java Programming Language (2024)
- Difference between Java and JavaScript?
- What is the difference between JDK and JRE?
- What gives Java its 'write once and run anywhere' nature?
- What is JVM and is it platform independent?
- What is Just-In-Time (JIT) compiler?
- What is the garbage collector in Java?
- What is NullPointerException in Java
- Difference between Stack and Heap memory in Java
- How to set the maximum memory usage for JVM?
- What is numeric promotion?
- Generics in Java
- Static keyword in Java
- What are final variables in Java?
- How Do Annotations Work in Java?
- How do I use the ternary operator in Java?
- What is instanceof keyword in Java?
- How ClassLoader Works in Java?
- What are fail-safe and fail-fast Iterators in Java
- What are method references in Java?
- "Cannot Find Symbol" compile error
- Difference between system.gc() and runtime.gc()
- How to convert TimeStamp to Date in Java?
- Does garbage collection guarantee that a program will not run out of memory?
- How setting an Object to null help Garbage Collection?
- How do objects become eligible for garbage collection?
- How to calculate date difference in Java
- Difference between Path and Classpath in Java
- Is Java "pass-by-reference" or "pass-by-value"?
- Difference between static and nonstatic methods java
- Why Java does not support pointers?
- What is a package in Java?
- What are wrapper classes in Java?
- What is singleton class in Java?
- Difference between Java Local Variable, Instance Variable and a Class Variable?
- Can a top level class be private or protected in Java
- Are Polymorphism , Overloading and Overriding similar concepts?
- Locking Mechanism in Java
- Why Multiple Inheritance is Not Supported in Java
- Why Java is not a pure Object Oriented language?
- Static class in Java
- Difference between Abstract class and Interface in Java
- Why do I need to override the equals and hashCode methods in Java?
- Why does Java not support operator overloading?
- Anonymous Classes in Java
- Static Vs Dynamic class loading in Java
- Why am I getting a NoClassDefFoundError in Java?
- How to Generate Random Number in Java
- What's the meaning of System.out.println in Java?
- What is the purpose of Runtime and System class in Java?
- The finally Block in Java
- Difference between final, finally and finalize
- What is try-with-resources in java?
- What is a stacktrace?
- Why String is immutable in Java ?
- What are different ways to create a string object in Java?
- Difference between String and StringBuffer/StringBuilder in Java
- Difference between creating String as new() and literal | Java
- How do I convert String to Date object in Java?
- How do I create a Java string from the contents of a file?
- What actually causes a StackOverflow error in Java?
- Why is char[] preferred over String for storage of password in Java
- What is I/O Filter and how do I use it in Java?
- Serialization and Deserialization in Java
- Understanding transient variables in Java
- What is Externalizable in Java?
- What is the purpose of serialization/deserialization in Java?
- How to append text to an existing file in Java
- How to convert InputStream object to a String in Java
- What is the difference between Reader and InputStream in Java
- Introduction to Java threads
- Synchronization in Java
- Static synchronization Vs non static synchronization in Java
- Deadlock in Java with Examples
- What is Daemon thread in Java
- Implement Runnable vs Extend Thread in Java
- What is the volatile keyword in Java
- What are the basic interfaces of Java Collections Framework
- Difference between ArrayList and Vector | Java
- What is the difference between ArrayList and LinkedList?
- What is the difference between List and Set in Java
- Difference between HashSet and HashMap in Java
- Difference between HashMap and Hashtable in Java?
- How does the hashCode() method of java works?
- Difference between capacity() and size() of Vector in Java
- What is a Java ClassNotFoundException?
- How to fix java.lang.UnsupportedClassVersionError