Unsupported major.minor version Error
The "Unsupported major.minor version" error occurs due to a mismatch in Java versions. This issue arises when a project is compiled on a higher Java version (e.g., JDK 1.8) and subsequently executed on a lower version (e.g., JDK 1.7). To address this error, there are two potential solutions: either recompile the code for an earlier Java version or run the code on a newer Java version. In situations where multiple Java SDK versions are installed on a system, it is crucial to ensure that the application being executed points to the appropriate or highest available version. For optimal compatibility, it is advisable to have both JRE/JDK components installed with the same version.

Java minor_version, major_version
The minor_version and major_version items in a Java class file represent the minor and major version numbers of the file, respectively. These version numbers collectively define the .class file format version. In this format, the combination of a major version (M) and a minor version (m) indicates the version of the .class file. Consequently, class file format versions can be sorted lexicographically, enabling comparison based on version numbers, such as 1.5 < 2.0 < 2.1.
Major version number of the class file format being used.
- Java SE 14 = 58 (0x3A hex)
- Java SE 13 = 57 (0x39 hex)
- Java SE 12 = 56 (0x38 hex)
- Java SE 11 = 55 (0x37 hex)
- Java SE 10 = 54 (0x36 hex)
- Java SE 9 = 53 (0x35 hex)
- Java SE 8 = 52 (0x34 hex)
- Java SE 7 = 51 (0x33 hex)
- Java SE 6.0 = 50 (0x32 hex)
- Java SE 5.0 = 49 (0x31 hex)
- JDK 1.4 = 48 (0x30 hex)
- JDK 1.3 = 47 (0x2F hex)
- JDK 1.2 = 46 (0x2E hex)
- JDK 1.1 = 45 (0x2D hex)
Java Compatibility
Java indeed places a strong emphasis on maintaining backward compatibility to ensure smooth evolution within its ecosystem. However, there are instances where changes that are not backward compatible become necessary to drive progress. Despite being backward compatible, it's essential to understand that certain version mismatches may still occur. While Java allows running class files or JAR files compiled in lower versions (e.g., Java 6) on higher versions (e.g., Java 8), the reverse is not always feasible. Running a class compiled with Java 7 on Java 5 may lead to errors since higher versions often introduce features that are unsupported in lower versions. Thus, it's crucial to consider version compatibility when executing Java applications across different versions.
For e.g. "Unsupported major.minor version 52.0" error occurs when attempting to execute a class compiled using the Java 1.8 compiler on a lower version of the Java Runtime Environment (JRE), such as JRE 1.7 or JRE 1.6. To address this issue, two potential solutions exist. Firstly, you can run the Java code using a more recent version of the Java JRE that matches the version used for compilation. Alternatively, you may specify the "target" parameter when invoking the Java compiler to instruct it to produce bytecode compatible with earlier Java versions, thus resolving the compatibility mismatch and enabling successful execution on lower JRE versions.
Eclipse
If you're using Eclipse you should do 2 things:
In Eclipse, click on Window > Preferences , and in the window that appears, on the left side, under Java , click on Installed JREs , click on Add... and navigate to the folder that contains the JDK.
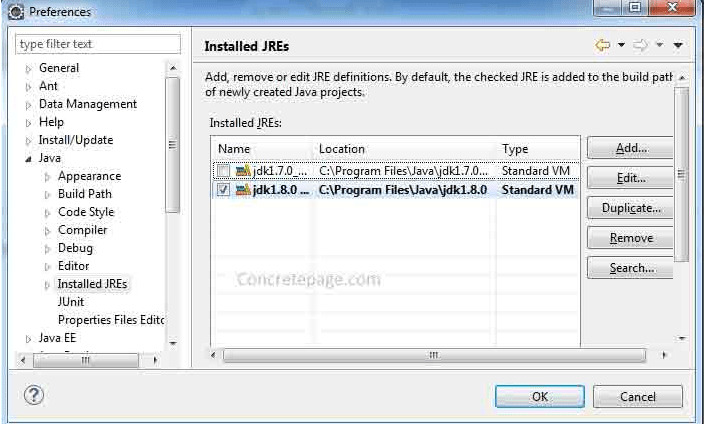
Select the check box to activate the required version of JRE.
Right-click on your project and click on Properties , in the window that appears, on the left side, click on Java Compiler and uncheck Use compliance from execution environment on the Java Build Path, this allows you to choose in the list Compiler compliance level the same version that you set in the previous step.
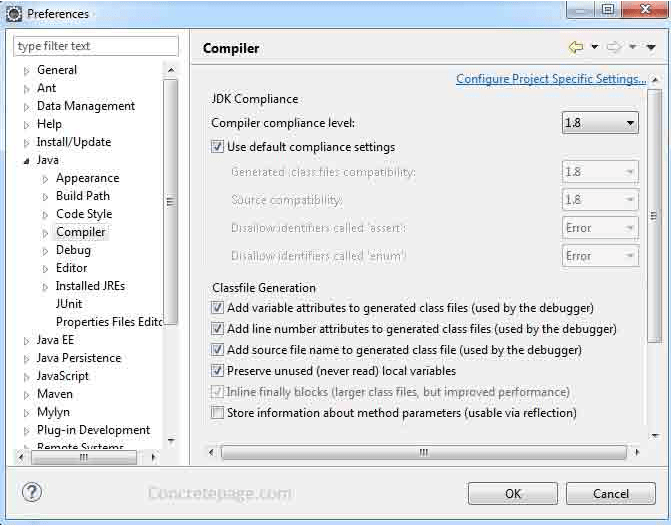
If the version of compiler compliance level and Installed JRE is different, eclipse gives the messages as follows. "When selecting 1.8 compliance, make sure to have a compatible JRE installed and activated (currently 1.7)"
Android Studio
If you have installed Android N , change Android rendering version with older one and the problem will disappear.
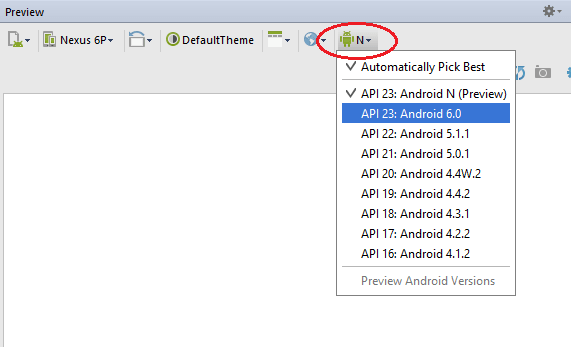
NetBeans
If you're using the NetBeans IDE , right click on the project and choose Properties and go to sources, and you can change the Source/Binary Format to a lower JDK version.
If you are using Maven , you can set the JDK version of each module by placing a file called nb-configuration.xml beside your pom.xml with the following content:
The "JDK_1.7" Java platform must be configured in Tools -> Java Platforms -> Add Platform .
Conclusion
The "Unsupported major.minor version" error occurs when trying to execute a Java class compiled with a higher version of the Java compiler on a lower version of the Java Runtime Environment (JRE). This error can be resolved by either using a newer version of the JRE matching the compiler's version or specifying the "target" parameter to the Java compiler to generate bytecode compatible with the desired JRE version.
- Java Interview Questions-Core Faq - 1
- Java Interview Questions-Core Faq - 2
- Java Interview Questions-Core Faq - 3
- Features of Java Programming Language (2024)
- Difference between Java and JavaScript?
- What is the difference between JDK and JRE?
- What gives Java its 'write once and run anywhere' nature?
- What is JVM and is it platform independent?
- What is Just-In-Time (JIT) compiler?
- What is the garbage collector in Java?
- What is NullPointerException in Java
- Difference between Stack and Heap memory in Java
- How to set the maximum memory usage for JVM?
- What is numeric promotion?
- Generics in Java
- Static keyword in Java
- What are final variables in Java?
- How Do Annotations Work in Java?
- How do I use the ternary operator in Java?
- What is instanceof keyword in Java?
- How ClassLoader Works in Java?
- What are fail-safe and fail-fast Iterators in Java
- What are method references in Java?
- "Cannot Find Symbol" compile error
- Difference between system.gc() and runtime.gc()
- How to convert TimeStamp to Date in Java?
- Does garbage collection guarantee that a program will not run out of memory?
- How setting an Object to null help Garbage Collection?
- How do objects become eligible for garbage collection?
- How to calculate date difference in Java
- Difference between Path and Classpath in Java
- Is Java "pass-by-reference" or "pass-by-value"?
- Difference between static and nonstatic methods java
- Why Java does not support pointers?
- What is a package in Java?
- What are wrapper classes in Java?
- What is singleton class in Java?
- Difference between Java Local Variable, Instance Variable and a Class Variable?
- Can a top level class be private or protected in Java
- Are Polymorphism , Overloading and Overriding similar concepts?
- Locking Mechanism in Java
- Why Multiple Inheritance is Not Supported in Java
- Why Java is not a pure Object Oriented language?
- Static class in Java
- Difference between Abstract class and Interface in Java
- Why do I need to override the equals and hashCode methods in Java?
- Why does Java not support operator overloading?
- Anonymous Classes in Java
- Static Vs Dynamic class loading in Java
- Why am I getting a NoClassDefFoundError in Java?
- How to Generate Random Number in Java
- What's the meaning of System.out.println in Java?
- What is the purpose of Runtime and System class in Java?
- The finally Block in Java
- Difference between final, finally and finalize
- What is try-with-resources in java?
- What is a stacktrace?
- Why String is immutable in Java ?
- What are different ways to create a string object in Java?
- Difference between String and StringBuffer/StringBuilder in Java
- Difference between creating String as new() and literal | Java
- How do I convert String to Date object in Java?
- How do I create a Java string from the contents of a file?
- What actually causes a StackOverflow error in Java?
- Why is char[] preferred over String for storage of password in Java
- What is I/O Filter and how do I use it in Java?
- Serialization and Deserialization in Java
- Understanding transient variables in Java
- What is Externalizable in Java?
- What is the purpose of serialization/deserialization in Java?
- What is the Difference between byte stream and Character streams
- How to append text to an existing file in Java
- How to convert InputStream object to a String in Java
- What is the difference between Reader and InputStream in Java
- Introduction to Java threads
- Synchronization in Java
- Static synchronization Vs non static synchronization in Java
- Deadlock in Java with Examples
- What is Daemon thread in Java
- Implement Runnable vs Extend Thread in Java
- What is the volatile keyword in Java
- What are the basic interfaces of Java Collections Framework
- Difference between ArrayList and Vector | Java
- What is the difference between ArrayList and LinkedList?
- What is the difference between List and Set in Java
- Difference between HashSet and HashMap in Java
- Difference between HashMap and Hashtable in Java?
- How does the hashCode() method of java works?
- Difference between capacity() and size() of Vector in Java
- What is a Java ClassNotFoundException?